MAKING A LIVING,
MAKING A DIFFERENCE 5
THINK AND DISCUSS (page 81)
Possible answers:
1. Tan Le’s invention could make it easier for people to operate electronic devices, including people with physical disabilities or limitations. For example, Le’s invention could help someone who cannot speak to communicate, or it could help a paralyzed person operate a wheelchair.
2. Earning income can improve not only one’s own life, but also the lives of family members. The money can be used to buy better food, better housing, or books and uniforms for school. A person can also make a difference by directly helping someone, as a doctor or teacher might. A person can also be a positive influence in a work environment.
EXPLORE THE THEME (page 82)
1. Answers will vary.
2. Possible answers: They are making a difference by providing goods and services that people need. The entrepreneurs may be designing software that is very helpful to people. The factory worker is being careful to produce a switch that gives people electricity. The bakery owner provides food and probably employs members of the community. The nurse provides care and comfort.
3. Answers will vary.
Lesson A
VOCABULARY
B (page 84)
1. conventional; 2. models; 3. cooperate; 4. profits; 5. diverse
C (page 84) Possible answers:
1. Owning the business could be quite motivating. Selling products or services together could lead to greater efficiencies and more profits. Sharing profits means that all members can earn a good living.
2. Profits could be higher through sharing expertise and advertising costs, and because workers/owners might have a greater incentive to do well
on the job. Profits could be lower if sharing profits means that costs (in the form of salaries) are higher.
3. I want the money I spend on products and services to go directly to the co-op members rather than to a corporation. I like the personal
attention I get by dealing with the co-op member-owners rather than with employees of a company. Or, I prefer the large selection or low
prices at large companies or stores.
D (page 84) Answers will vary.
E (page 85)
1. poverty; 2. entrepreneurs; 3. generate; 4. effective; 5. assess
F (page 85)
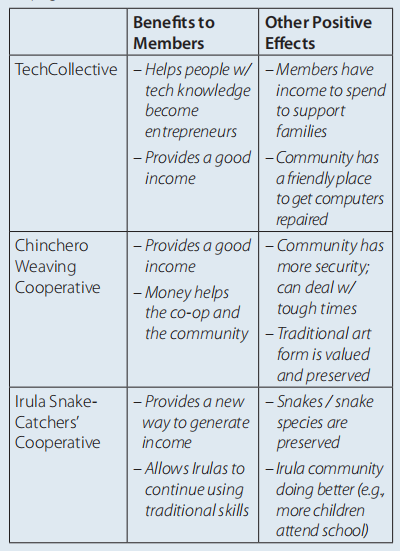
1. Forming the weaving cooperative created an additional source and new of income for people in Chinchero. It allowed the women of Chinchero to earn money from their traditional craft.
2. Possible answers: Having diverse kinds of businesses in a community means more choices for customers and more employment options
for workers—whether they prefer to work for themselves, to work for a small business, or to work for a large company.
G (page 85)
Cooperative, interactive, attractive, communicative,
expressive, protective. Example sentences will vary.
LISTENING
A (page 86) Possible answers:
1. Wildlife was probably becoming endangered and needed protection; India recognized the value of protecting wild plants and animals from human activity.
2. An employer goes out of business. A job doesn’t pay enough to support a growing family. Broader economic changes take place (e.g., imported goods replace local products). Physical limitations or aging make it harder to do a certain job. Moving to another city or country means leaving a job behind.
B (page 87) Possible answers:
1. dir.; 2. info.; 3. Ind.; 4. pov. / pov’ty; 5. entre’s / ent’prnrs; 6. hum.
C (page 87)
1. b; 2. c; 3. b; 4. a
D (page 87) Possible answers:

SPEAKING
B (page 88)
1. [50,000] fifty thousand
2. [3,200,000] three point two million / three million, two hundred thousand
3. [9,600] ninety-six hundred / nine thousand six hundred
4. [740,000] seven hundred (and) forty thousand
5. [8,000,000,000] eight billion
6. [1,297,300] one million, two hundred (and) ninetyseven thousand, (and) three hundred
C (page 88)
1. 85; 2. 60; 3. 18; 4. 2,500; 5. 7.4
D (page 89)
1. Answers will vary.
2. Possible answers: The Irula Snake Catchers’ co-op and Basket’s kudzu business are both environmentally friendly. On the other hand, Basket works alone while hundreds of snake catchers work for the co-op. Another difference is that Basket’s products may be nice and useful,
but they don’t save lives like the anti-venom produced by the snake catchers.
3. Possible answers: If kudzu products became quite popular, kudzu entrepreneurs might make a difference in the amount of kudzu growing in the U.S., but one kudzu entrepreneur probably can’t use very much of approximately 7.4 million acres of kudzu.
4. Possible answers:
- Marketing and advertising a product makes buyers aware of the product and leads to sales.
- Maintaining a website is an extremely important way to reach potential clients.
- Managing employees is part of making any business run smoothly. Happy and well-trained employees contribute to the success of a business.
- Getting supplies is necessary before products can be produced.
- Selling and shipping products gets them into the hands of customers.
- Doing accounting and paying taxes are essential to a company’s financial health and its legal operation.
Small business owners might also do research to make good decisions about developing new products or services, or they might write a newsletter or send marketing e-mails to their clients to encourage future
business.
E (page 90)
1. 5,825,458: five million, eight hundred (and) twenty-five thousand, four hundred (and) fiftyeight
2. 19, 076: nineteen thousand (and) seventy-six
3. around 60 million
4. The overall number decreased somewhat. The economy may not have been very strong at that time, or it might have been difficult to get loans
to start new businesses.
5. Four hundred thousand, six hundred (and) eighty-seven businesses closed in 2013, which is fewer than the four hundred ninety-three
thousand, nine hundred (and) ninety-four that closed in 2009. The economy might have been improving, and perhaps people were spending more money in 2013.
6. The number decreased substantially, from fifty-eight thousand, seven hundred (and) twenty-one in 2009 to thirty-six thousand, (and) sixty-one in 2013. The economy may have been improving, and more businesses were doing well.
7. Answers will vary.
LESSON TASK
A (page 91) Possible answers:
All small businesses would provide employment and the convenience of having something close by in the community.
Restaurants and coffee shops: fresh food; a place to socialize with friends and family
Retail shops: a place to buy specific things
Manufacturers: sources of new products and employment
Service providers: a place to get something repaired or get assistance with something
B (page 91) Answers will vary.
C (page 91) Answers will vary.
Video
A (page 92)
1. lack; 2. infrastructure; 3. extend; 4. kerosene;
5. working conditions
B (page 92)
Possible answers: People who live off-grid would not have a television or radio for news or entertainment, and they would not be able to study or work at night. Even charging the batteries in computers or telephones would be impossible. Everyday chores such as laundry or house-keeping would require more labor, since washing machines or other conveniences could not be used.
C (page 93)
1. T
2. T
3. F (a lot of money)
4. F (does not require any new land)
D (page 93) Answers will vary.
E (page 93)
1. 200,000,000 (or 200 million) / 60; 2. 30; 3. 1,000; 4. 3,500 / 140
F (page 93)
1. Possible answers: Cooling: air conditioners,
fans; Heating: space heaters, radiators; Lighting:
lamps, overhead lighting; Work or entertainment:
computers, TVs; Cleaning: washers, dryers,
vacuum cleaners; Water heating: showers, baths;
Cooking: refrigeration, stovetop, oven, microwave
2. Answers will vary.
3. Answers will vary.
Lesson B
VOCABULARY
B (page 94)
1. concept, fundamental
2. response
3. corporation
4. donate, charity
5. accessible
6. demonstrate
7. outcome
8. affordable
C (page 95)
1. concept
2. donate
3. charity
4. affordable
5. fundamental
6. demonstrate
7. response
D (page 95)
1. Answers will vary.
2. Possible answers: They can donate goods to local thrift or second-hand stores. They can lend or rent something out for a low price when they are not using it, such as a bicycle, car, or apartment.
They can pass out a questionnaire asking what people need and then host community events to collect those items.
LISTENING
A (page 96) Answers will vary.
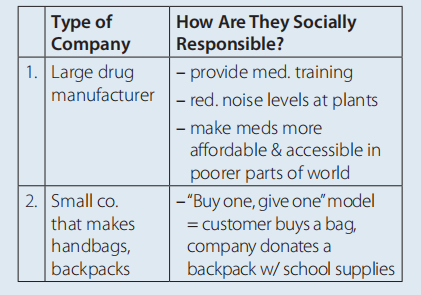
B (page 96) Possible answers:

C (page 97)
1. both; 2. though; 3. too; 4. Even though
D (page 97)
1. Answers will vary.
2. Possible answers:
a. Reducing their use of paper would help decrease their environmental impact.
b. Providing free software to help local charities would help strengthen their community.
c. Offering free after-school classes would help them give back to their customers’ families and prepare youth for a competitive job market.
SPEAKING
A (page 98) Possible answers:
1. Do you know what time it is?
2. I’d like to know why you are taking this class.
3. Can you tell me how old you were when you took your first English class?
4. Could you tell me what kind of career you hope to have in the future?
5. Can you tell me how you make decisions about the clothing you buy?
6. I’m wondering where I should go for a day trip this weekend.
B (page 99) Possible answers:
1. I’d like to know what technology company is the most influential.
2. Could you explain how people get jobs with good companies?
3. I’m wondering whether you would want to be a member of a cooperative.
4. Can you tell me what kind of small business you would like to start?
C (page 99) Answers will vary.
D (page 99) Answers will vary.
FINAL TASK
A–C (page 100) Answers will vary.
