UNIT 1 URBAN CHALLENGES
THINK AND DISCUSS (page 1)
1. Possible Answers: Green buildings are intended to solve the
challenges of urban pollution and energy waste. In addition
to special windows, many green buildings catch and store
rainwater in big containers to be used to water plants or flush
toilets.
2. Answers will vary.
EXPLORE THE THEME (pages 2–3)
1. Possible answers: A cosmopolitan hotspot is an urban area
with residents, often foreign born, who come from a variety of
cultures and ethnicities and who speak a variety of languages.
A tourism hotspot is an urban area that receives at least two
million visitors in a year. It is a place where people from all over
the world come to visit.
2. Answers will vary.
3. Answers will vary.
4. Possible answers: Residents of cosmopolitan hotspots could
face challenges such as language barriers, cultural tensions,
competition for jobs and housing, etc. Residents of tourism
hotspots could face challenges such as crowded streets and
other public spaces, increased prices for food and drinks,
increased housing costs, etc.
LESSON A
Vocabulary
B (page 4)
1. c
2. h
3. f
4. i
5. g
6. d
7. e
8. j
9. a
10. b
C (page 5)

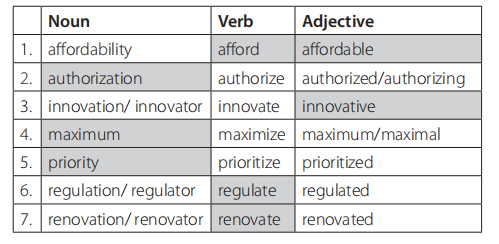
D (page 5)
Possible answers:


BEFORE LISTENING
A Predicting (page 6)
Possible answers:
Around 25 million tourists visit Venice each year. Tourists help the city by generating a lot of revenue that can be used to address some of the city’s problems. Tourism also creates many jobs. Tourists hurt the city by leaving trash, filling public parking lots, and making boats and gondolas, which are the primary means of public transportation, crowded. Tourism has led to inflation of prices, the replacement of local shops with souvenir shops, increased rents, and a lack of affordable housing for the local population, which is rapidly shrinking.
WHILE LISTENING
B (page 6)
1. b
2. c
C Listening for Main Ideas (page 7)
1. P the impact of tourism on city services
4. P the effects of tourism on residents of Venice
6. P the benefits of tourism for Venice
D Note Taking (page 7)
1. =
2. B or bil
3. w/ or =
4. pos or +
5. neg or -
6. ~
7. M or mil
8. K
E Critical Thinking: Reflecting (page 7)
Possible answers:
Shortening words to their first several letters (cent, Ven),
acronyms (MOSE), symbols ($), numbers (5, 25, 1, 80), chemistry
abbreviations (H2O), removing vowels (wknd)
F Critical Thinking: Making Inferences (page 7)
Possible answers:
1. Their attitude is conflicted, or mixed. On the one hand, tourists
make life inconvenient and sometimes difficult for residents.
On the other hand, it’s unclear how the city would be doing
without the revenue that tourism brings in.
2. The lecturer feels the fate of Venice is really in its own hands
and that the city needs to make a firm decision about what
its priority is rather than trying to maintain two conflicting
priorities.
A SPEAKING
A (page 8)
1. Public transportation/Transportation
2. Inflation
3. housing problem(s)
4. projects
5. jobs
B Critical Thinking: Applying (page 8)
Answers will vary.
C Critical Thinking: Analyzing Visuals (page 9)
1. are located
2. stay
3. are raised
4. are forecast
5. is pumped
6. move
7. be adjusted
8. are lowered
D (page 9)
Answers will vary.
E (page 9)
Possible answers:
Yes. It may not stop the floods completely, but it could create
enough of a barrier between the city and the floodwaters
to prevent major danger and damage. Some other defenses
cities can use to prevent flooding are to line coastal areas with
sandbags, plan for infrastructure to be built well above sea level,
have an efficient water drainage system, etc.
F (page 10)
Answers will vary.
LESSON TASK Evaluating the Impact of Tourism
A–C (pages 10–11)
Answers will vary
VIDEO Urban Solution: Farming on Rooftops
BEFORE VIEWING
A Critical Thinking: Predicting (page 12)
Possible answers:
1. It’s a way of making use of industrial buildings; it has a
tremendous benefit to the ecosystem; it reduces “urban heat
island effect”; it cleans the air; it decreases the amount of HVAC
of the buildings’ upper floors; it links people back to their food
production system; it makes a city healthier, more beautiful,
and more delicious.
2. Raising chickens and harvesting their eggs; beekeeping and
harvesting honey
B (page 13)
1. e
2. a
3. b
4. c
5. d
WHILE VIEWING
C Understanding Main Ideas (page 13)
2. P Ben Flanner discovered his passion for farming when he came
to New York City.
3. P The farmers have given consideration to the soil and water.
4. P Rooftop farms connect the community with the production
of its food.
D Understanding Details (page 13)
1. (a) small scale
2. bees
3. several weeks
4. They are lighter./They weigh less.
5. one million gallons
6. They reduce it.
E Checking Predictions (page 13)
Answers will vary.
AFTER VIEWING
F Personalizing (page 13)
Answers will vary.
LESSON B
Vocabulary
A (page 14)
1. i
2. d
3. j
4. h
5. e
6. c
7. a
8. f
9. b
10. g
B (page 14)
1. ranks
2. affluent
3. dominant
4. ethnic
5. enforced
6. restricted
7. are unique to
8. internalized
9. conform
10. debatable
C (page 15)

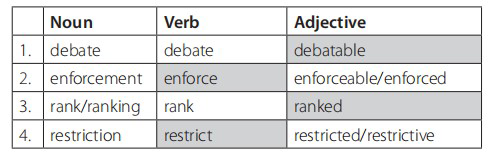
1. restricted
2. debate
3. enforce
4. ranked
D (page 15)
1. T
2. F (The largest ethnic group in Singapore is Chinese.)
3. F (It is not restricted.)
4. T
E Personalizing (page 15)
Answers will vary.
B LISTENING A Conversation about Singapore
BEFORE LISTENING
A Critical Thinking: Predicting (page 16)
Possible answers:
1. banking, finance, tourism
2. A city-state is a city that, along with its surrounding area, is
considered to be an independent state or country.
3. The symbol blends the body of a fish with the head of a lion
to reflect its origins as a fishing village and its original name,
Singapura, which means “lion city.”
WHILE LISTENING
B Listening for Main Ideas (page 16)
1. T
2. F
3. F
4. F
5. T
6. T
C (page 16)
2. Singapore does not have a lot of natural resources.
3. The people of Singapore belong to many different ethnic groups.
4. The spirit of kiasu means “afraid to lose.”
D Listening for Details (page 17)
1. fishing village
2. 1819
3. 270
4. 100
5. 2nd, second
6. Singapore politics/politics/Singapore
7. to lose
AFTER LISTENING
E Personalizing (page 17)
Answers will vary.
F Critical Thinking: Evaluating (page 17)
Possible answers:
1. purpose = prevent previously chewed gum from dirtying sidewalks
2. purpose = keep sidewalks clean; for good hygiene
3. purpose = control noise pollution
4. purpose = discourage dishonesty
5. purpose = maintain cleanliness in public places; sanitation
6. purpose = prevent the spread of mosquito-borne diseases
7. purpose = prevent the mess made by pigeon droppings; sanitation
G Personalizing (page 17)
Answers will vary.
B SPEAKING
A (page 18)


C (page 18)
1. didn’t hear (no air); what you (like ch); about which (no air); it again (like a quick d)
2. want some (no air); about some (no air)
3. About that (no air); that budget (no air); budget I (like a quick d); it been (no air)
4. What are (like a quick d); that ad (like a quick d); put it (like a quick d)
5. What are (like a quick d); upset about (like a quick d)
6. Haven’t you (like ch), that project (no air)
D Critical Thinking: Evaluating (page 19)
Answers will vary.
FINAL TASK Presenting a Problem and Solutions
A–E (pages 19–20)
Answers will vary.
