9 SPECIES SURVIVAL
Think and Discuss (page 161)
1. Its color and its poisonous spines keep its enemies away and help it to survive.
2. Possible answer: It means that the unit will discuss the things that help animals to survive in the world and not go extinct.
3. Answers will vary.
EXPLORE THE THEME (pages 162–163)
1. Animals use color to match their surroundings (camouflage), to attract a mate, and to tell predators that they are poisonous.
2. It helps it to reach leaves to eat and to see its predators.
3. Answers will vary.
4. Possible answers: House cats domesticated, or became pets, in order to survive. Now humans protect them. Some animals, such as the pufferfish, can appear larger than they really are to scare away
predators.
Lesson A
VOCABULARY
B (page 164) 1. differed; 2. identify; 3. offspring;
4. diversity; 5. traits; 6. reproduce; 7. adapt;
8. species; 9. process; 10. inherit
C (page 165) 1. diversity; 2. reproduced; 3. inherited;
4. traits; 5. process
D (page 165)
1.–2. Answers will vary.
3. Possible answer: Giant pandas are a species of bear that live in China.
4. Answers will vary.
5. Possible answer: Countries with rainforests, like Brazil in South America and Indonesia in Southeast Asia, have a large diversity of plant and animal species.
LISTENING
A (page 166) Answers will vary.
B (page 166) All of the words in the box should be checked.
√ Different finches have different traits that help them survive and reproduce. (main idea)
C (page 167) Possible answers:

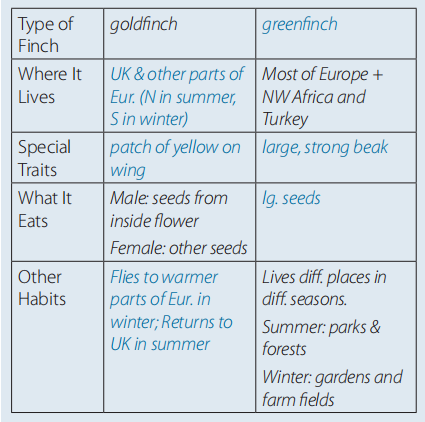
E (page 167) Possible answers:
Where It Lives: The European goldfinch lives in the United Kingdom and other parts of Europe—in northern Europe during the summer, and farther south during the winter. The greenfinch lives in most parts of Europe, and also in northwest Africa and parts of Turkey.
Special Traits: The goldfinch has a patch of bright yellow feathers on each wing. The greenfinch has a large, powerful beak.
What It Eats: The male goldfinch eats the small seeds inside flowers, the female goldfinch eats other small seeds, and the greenfinch eats larger seeds.
Other Habits: Goldfinches fly to warmer parts of Europe in September or October. They return to the United Kingdom in the spring. Greenfinches don’t leave in the winter, but they live in different places during different seasons. In the summer, they live in parks and forests. In the winter, they live in people’s gardens and in farmers’ fields where they can find
food.
F (page 167) Answers will vary.
SPEAKING
A (page 168) 1. ba-na-na (3 syllables); de-mand (2 syllables); i-den-ti-fy (4 syllables); re-pro-duce (3 syllables) 2. Bold syllables are stressed. ba-na-na; de-mand; i-den-ti-fy; re-pro-duce 3. banana (2 different vowel sounds, with two schwas /bә’næ-nә/); demand (2 different vowel sounds
/dә’mænd/); identify (3 different vowel sounds, the same at the beginning and end /aɪ’dɛn-tә-faɪ/); reproduce (3 different vowel sounds = /ri-prә’dus/)
B (page 168) 1. practical; 2. compare; 3. attachment; 4. available;
5. proportion; 6. support
C (page 168)


D (page 168) Answers will vary.
E (page 169)
2. Because of this 3. therefore 5. as a result
G (page 170)
1. The blue wildebeest is threatened by lions, leopards, and other predators. The dead leaf butterfly is threatened by birds and other insects. The Texas horned lizard is threatened by snakes, hawks, and coyotes. The opossum is threatened by people, cats, and other predators.
2. The blue wildebeest runs fast. The dead leaf butterfly uses camouflage to avoid being seen. The Texas horned lizard shoots blood from its
eyes. The opossum lives in trees, is nocturnal, can play dead, and may even smell bad.
3. Answers will vary.
H (page 171) Possible answers:
1. Since lions and leopards eat blue wildebeests, the wildebeests need to run very fast.
2. The butterfly looks like a dead leaf, so predators don’t recognize it as food.
3. The lizard can surprise its predators; as a result, the lizard has the chance to escape.
4. The opossum has several survival behaviors. Consequently, it is less likely to be killed or eaten by predators.
5. Because the opossum seems to be dead, predators don’t want to eat it.
LESSON TASK
A–C (page 171) Answers will vary.
Video
B (page 172) 1. branches; 2. rotate; 3. mimic; 4. project; 5. background
C (page 173) 1. T; 2. F (Females change colors when they are not interested in a male.); 3. F (Chameleons move in a way that mimics a leaf or branch in the wind.); 4. T
D (page 173) 1. 202, 42; 2. 2; 3. 13; 4. 36; 5. 9, 37
E (page 173)
1. Changes to habitat, deforestation, and other pressures on habitat are directly related to human activity.
2. Possible answer: They could stop cutting down forests to create farmland and produce less waste.
3. Answers will vary.
Lesson B
VOCABULARY
B (page 175) 1. aware; 2. classify; 3. variations;
4. technique; 5. controversial; 6. sample; 7. gene;
8. substances; 9. sequences; 10. argued
C (page 175) 1.–3. Answers will vary.
4. People can organize educational events or throw animal-themed parties.
D (page 175)
1. definition 1
2. Answers will vary, but students should find more than one definition for each word.
LISTENING
A (page 176) Answers will vary.
B (page 176) 1. F (He wants to photograph all of the species that are in human care.); 2. T; 3. F (It shows images of animals in zoos or in captivity.); 4. T
C (page 177) 1. Y; 2. N; 3. Y; 4. Y
D (page 177) Answers will vary.
SPEAKING
B (page 179) Possible answers:
talk into = to persuade someone to do something
turn down = to reject or say no to something or someone
set up = to put in place or the correct order for use
clear up = to become brighter; stop raining
turn on = to activate
pick up = to lift up
D (page 179) 1. talked, into; 2. pick, up; 3. set up;
4. cleared up; 5. turn on; 6. turned down
FINAL TASK
A–C (pages 179–180) Answers will vary.
