10 HOW WE COMMUNICATE
THINK AND DISCUSS (page 181) Possible answers:
1. They are trying to get a signal so they can use their cell phones.
2. Cell phones and computers have made it easier and faster to communicate. But we write fewer letters now, and probably have less direct communication with people than we used to before we had them.
3. How technology has changed communication, and the effects of these changes.
EXPLORE THE THEME (pages 182–183)
1. The percentage of people who have access to the Internet.
2. North America, Europe, and Australia have the most access. Some parts of Africa and Asia have the least.
3. Answers will vary.
Lesson A
VOCABULARY
A (page 184) 1. involve; 2. speed; 3. connect;
4. represent; 5. wide; 6. inform; 7. basic; 8. contact;
9. access; 10. according to
B (page 184) 1. basic; 2. contact; 3. wide; 4. access;
5. According to; 6. involve; 7. connect; 8. inform;
9. represents; 10. speed
C (page 185)
1. Possible answer: I usually contact people through email, text messaging, social media, and phone calls.
2. Possible answers: Some animals move at a slow speed, like sloths and turtles. The Internet usually moves at a high speed.
3. Possible answers: A smartphone has Internet access, can record audio and video, can take pictures, and has a keyboard to type out
messages. People use smartphones for basic communication like calls and texts, but also to research things and connect with people all over
the world on social media.
4. a. # means “number”
b. & means “and”
c. + means “also, in addition to, plus”
d. % means “percentage”
e. @ means “at”
D (page 185) 1. access; 2. contact; 3. connect; 4. involve
E (page 185)
1.–2. Answers will vary.
3. Possible answer: Reading different sources and listening to different points of views about a topic can help someone get a basic understanding.
4. Possible answer: Having many interests allows you to connect with more people, but having too many means it’s difficult to really focus on
any one.
LISTENING
A (page 186)
It’s amazing! / All you need / is a laptop computer, / a cell phone, / and a cable, / and you have a communication system / with a wide reach. / With Banks’s software installed on the computer, / the cell phone sends text messages / to thousands of people at once, / without involving the Internet.
B (page 186) Answers will vary based on students’ speech. Answers based on audio:
1. Professor Jones is the oldest professor / at the university.
2. I almost never / send a real letter to anyone.
3. Lily has a phone, / but she doesn’t have a computer.
4. We had a good conversation / about our families.
5. Tom and Marsha / are my only friends in the city.
6. The assignment is to read a chapter / and write some questions for discussion.
C (page 186) Answers will vary.
D (page 187)
access: 5
cellular/cell phone: 3
communicate/communication: 5
computer: 2
inform/information: 5
software: 6
Main idea:
√ Banks invented software that helped people communicate without the Internet.
E (page 187) 1. F (The UN says access to the Internet is a basic human right.); 2. T; 3. F (People have created different ways to use his software.); 4. T
F (page 187) Answers will vary.
SPEAKING
A (page 188)
1. The Morgans have/The Morgans’ve traveled to Europe four times.
2. Celine has not/hasn’t visited her family in Romania since 2009.
3. Randal has/Randal’s cooked a delicious meal. Can you join us for dinner?
4. I have not/haven’t seen the new action movie. Let’s go see it tonight!
5. He has/He’s called me twice today.
6. They have/They’ve known each other for a long time.
B (page 188) 1. since; 2. for; 3. for; 4. since
C (page 189) Events should be organized in the
following order:
1824, Braille system
1876, Telephone and microphone
1892, Motion picture projector
1896, Early form of radio
1927, Television
1971, Personal computer
1973, Cellular telephone
1989, World Wide Web
D (pages 189–190)
1. been; 2. 1824; 3. existed; 4. Possible answer: 142;
5. has; 6. since; 5. had; 6. 1973
E (page 190) Answers will vary. Students should discuss the following inventions: motion picture projector, radio, personal computer, microphone, the World Wide Web
F (page 190) Answers will vary.
LESSON TASK
A–C (page 191) Answers will vary.
Video
A (page 192) Possible answers:
1. Animals might communicate for some of the same reasons as humans: to meet up or to warn each other about danger.
2. They use sounds like when a dog barks or a cat meows. They also use non-verbal communication like when a peacock fans its feathers or a dolphin slaps the water.
3. People also use sounds or body movements to communicate, but they use words more.
B (page 193) Answers will vary.
C (page 193) 1. tusking the ground; 2. an invitation to play; 3. being social; 4. lies on the ground; 5. are tolerant
D (page 193) 1. d 2. c; 3. d; 4. b; 5. a
E (page 193) Possible answers:
1. She seems to really enjoy her work. She is very interested in elephants. She seems to care a lot about them and their safety, and she finds them
funny and interesting.
2. Elephants love climbing on each other, being social, and playing when they’re feeling good. A lot of their communication is through floppy and
wiggly movements.
3. Play helps people and animals develop social skills and learn boundaries.
4. Insects like ants and bees have organized social groups and complex communication.
Lesson B
VOCABULARY
B (page 194) 1. experts; 2. sign; 3. express;
4. importance; 5. support; 6. point; 7. recent;
8. speech; 9. pay attention to; 10. in addition to
C (page 195)

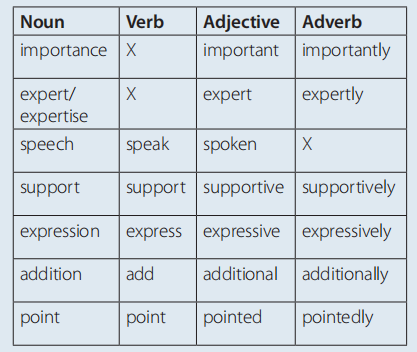
D (page 195) 1. importance; 2. speak; 3. expert;
4. supports; 5. point; 6. expression
E (page 195) Answers will vary.
LISTENING
A (page 196) Answers will vary.
B (page 196) 1. F; 2. F; 3. T; 4. T; 5. F
C (page 197)

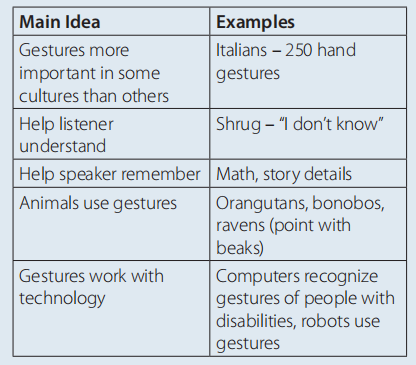
D (page 197) Answers will vary.
E (page 197) Possible answer:
We can conclude that programmers are teaching computers and robots to recognize and understand the meaning of gestures. Gestures are so important to human understanding that they may make communication between people and computers and robots more effective as well.
SPEAKING
A (page 198) The following sentences should be
underlined:
Do you see what I mean? Does that make sense?
Got it?
B (page 199) 1. make; 2. mean; 3. following/with
The following phrases should be underlined:
Does that make sense? Do you see what I mean? Are
you following me/with me?
C–D (page 199) Answers will vary.
FINAL TASK
A–C (page 200) Answers will vary.
