商品详情









内容提要:
本书由以下内容构成:
4套完整的学术类以及2套培训类阅读及写作部分雅思全真试题
各种题型的介绍以及剑桥大学考试委员会采用的评分系统解析
习题答案和听力录音文本
考生作文及考官点评
扫描封面内侧二维码,获取听力题目音频。
本书采用“一书一码”防伪形式,每个二维码仅绑定一个账号,一经绑定,学习资源仅供账号所有者在线使用,转让无效。
编辑推荐
准备任何一门考试,关键就是要研究真题:只有了解考试考什么,才知道怎么去准备。《剑桥雅思官方真题集10》由雅思考试命题方出品,是官方出版的相当具有参考价值的雅思备考资料。书中含4套完整的学术类以及2套培训类阅读及写作部分雅思全真试题,并提供习题解答和听力录音文本,写作部分提供考生作文及考官点评,适合考生自学。此外,书中还包含对各种题型的全面介绍、对剑桥大学考试委员会采用的评分系统的解析以及音频线上资源。本书所有资料均由剑桥大学考试委员会英语考评部提供,是雅思考生备考过程中必不可少的参考书。
优势卖点
剑桥大学出版社是出版剑桥大学考试委员会各类考试(包括雅思)历届考试真题的指定官方出版社。
本书所包含的雅思全真试题资料由剑桥大学考试委员会英语考评部提供,是雅思考生备考过程中必不可少的参考书。
适合考生自学的习题解答和听力录音文本。
可影印使用的答题卡,方便考生体验真实的考试模式。
扫描封面内侧二维码,可在线使用线上音频资源。

作者简介:
剑桥考试联合出版中心(Cambridge Exams Publishing)是由剑桥大学出版社和剑桥大学英语考评部共同成立的。
剑桥大学出版社(Cambridge University Press):剑桥大学出版社是出版剑桥大学考试委员会各类考试(包括雅思)历届考试真题的官方指定出版社。
剑桥大学英语考评部(Cambridge Assessment English):隶属于剑桥大学考试委员会,拥有100多年的语言教学和测评经验,在130多个国家提供一系列学术、职业和技能的证书考试,在世界范围内得到了移民机构、教育机构、政府及企业的广泛认可。
目录:
Introduction 4
Test 1 10
Test 2 33
Test 3 57
Test 4 80
General Training: Reading and Writing Test A 104
General Training: Reading and Writing Test B 117
Audioscripts 130
Listening and Reading Answer Keys 151
Model and sample answers for Writing tasks 161
Sample answer sheets 173
Acknowledgements 177
在线试读:
The International English Language Testing System (IELTS) is widely recognised as a reliable means of assessing the language ability of candidates who need to study or work where English is the language of communication. These Practice Tests are designed to give future IELTS candidates an idea of whether their English is at the required level.
IELTS is owned by three partners, Cambridge English Language Assessment, part of the University of Cambridge, the British Council and IDP Education Pty Limited (through its subsidiary company, IELTS Australia Pty Limited). Further information on IELTS can be found on the IELTS website www.ielts.org.
WHAT IS THE TEST FORMAT?
IELTS consists of four components. All candidates take the same Listening and Speaking tests. There is a choice of Reading and Writing tests according to whether a candidate is taking the Academic or General Training module.
Academic
For candidates wishing to study at undergraduate or postgraduate levels, and for those seeking professional registration.
General Training
For candidates wishing to migrate to an English-speaking country (Australia, Canada, New Zealand, UK), and for those wishing to train or study at below degree level.
The test components are taken in the following order:
Listening
4 parts, 40 items approximately 30 minutes
Academic Reading
3 sections, 40 items
60 minutes or General Training Reading
3 sections, 40 items
60 minutes
Academic Writing
2 tasks
60 minutes or General Training Writing
2 tasks
60 minutes
Speaking
11 to 14 minutes
Total Test Time
2 hours 44 minutes
General Training TEST FORMAT
Listening
This test consists of four parts, each with ten questions. The first two parts are concerned with social needs. The first part is a conversation between two speakers and the second part is a monologue. The final two parts are concerned with situations related to educational or training contexts. The third part is a conversation between up to four people and the fourth part is a monologue.
A variety of question types is used, including: multiple choice, matching, plan/map/diagram labelling, form completion, note completion, table completion, flow-chart completion, summary completion, sentence completion, short-answer questions.
Candidates hear the recording once only and answer the questions as they listen. Ten minutes are allowed at the end for candidates to transfer their answers to the answer sheet.
Academic Reading
This test consists of three sections with 40 questions. The texts are taken from notices, advertisements, leaflets, newspapers, instruction manuals, books and magazines. The first section contains texts relevant to basic linguistic survival in English, with tasks mainly concerned with providing factual information. The second section focuses on the work context and involves texts of more complex language. The third section involves reading more extended text, with a more complex structure, but with the emphasis on descriptive and instructive rather than argumentative texts.
A variety of question types is used, including: multiple choice, identifying information (True/False/Not Given), identifying writer’s views/claims (Yes/No/Not Given), matching information, matching headings, matching features, matching sentence endings, sentence completion, summary completion, note completion, table completion, flow-chart completion, diagram label completion, short-answer questions.
General Training Reading
This test consists of three sections with 40 questions. The texts are taken from notices, advertisements, leaflets, newspapers, instruction manuals, books and magazines. The first section contains texts relevant to basic linguistic survival in English, with tasks mainly concerned with providing factual information. The second section focuses on the work context and involves texts of more complex language. The third section involves reading more extended texts, with a more complex structure, but with the emphasis on descriptive and instructive rather than argumentative texts.
A variety of question types is used, including: multiple choice, identifying information (True/False/Not Given), identifying the writer’s views/claims (Yes/No/Not Given), matching information, matching headings, matching features, matching sentence endings, sentence completion, summary completion, note completion, table completion, flow-chart completion, diagram label completion, short-answer questions.
Academic Writing
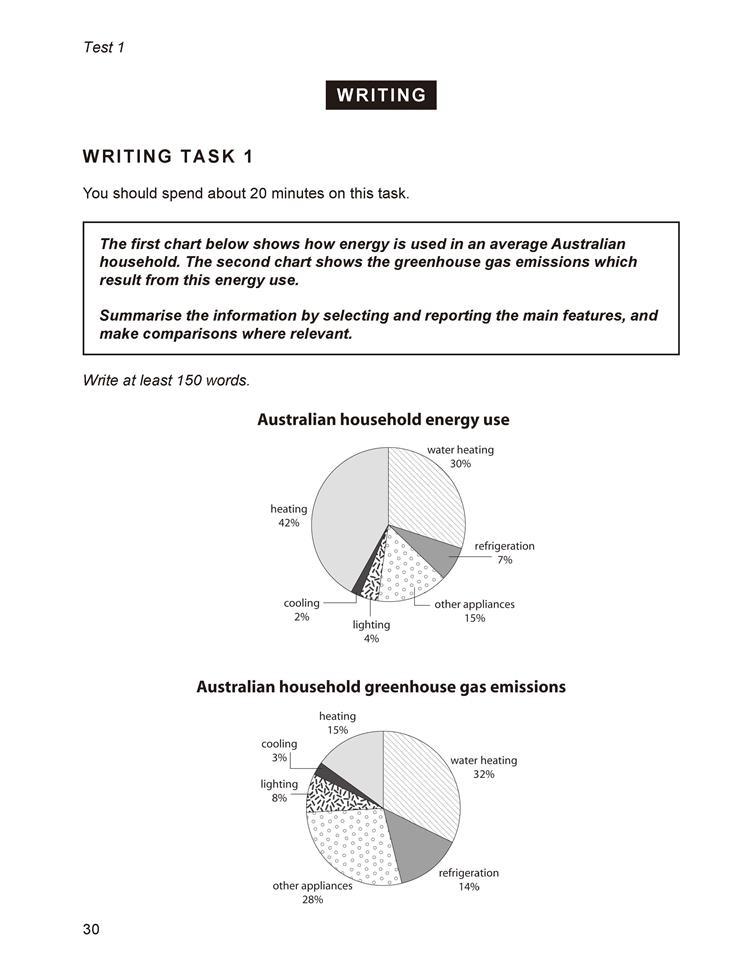
This test consists of two tasks. It is suggested that candidates spend about 20 minutes on Task 1, which requires them to write at least 150 words, and 40 minutes on Task 2, which requires them to write at least 250 words. Task 2 contributes twice as much as Task 1 to the Writing score.
In Task 1, candidates are asked to respond to a given situation with a letter requesting information or explaining the situation. They are assessed on their ability to engage in personal correspondence, elicit and provide general factual information, express needs, wants, likes and dislikes, express opinions, complaints, etc.
In Task 2, candidates are presented with a point of view, argument or problem. They are assessed on their ability to provide general factual information, outline a problem and present a solution, present and justify an opinion, and to evaluate and challenge ideas, evidence or arguments.
Candidates are also assessed on their ability to write in an appropriate style.
General Training Writing
This test consists of two tasks. It is suggested that candidates spend about 20 minutes on Task 1, which requires them to write at least 150 words, and 40 minutes on Task 2, which requires them to write at least 250 words. Task 2 contributes twice as much as Task 1 to the Writing score.
In Task 1 candidates are asked to respond to a given situation with a letter requesting information or explaining the situation. They are assessed on their ability to engage in personal correspondence, elicit and provide general factual information, express needs, wants, likes and dislikes, express opinions, complaints, etc.
In Task 2 candidates are presented with a point of view, argument or problem. They are assessed on their ability to provide general factual information, outline a problem and present a solution, present and justify an opinion, evaluate and challenge ideas, evidence or arguments.
Candidates are also assessed on their ability to write in an appropriate style.
More information on assessing both the Academic and General Training Writing tests, including Writing Assessment Criteria (public version), is available on the IELTS website.
Speaking
This test takes between 11 and 14 minutes and is conducted by a trained examiner.
There are three parts:
Part 1
The candidate and the examiner introduce themselves. Candidates then answer general questions about themselves, their home/family, their job/studies, their interests and a wide range of similar familiar topic areas. This part lasts between four and five minutes.
Part 2
The candidate is given a task card with prompts and is asked to talk on a particular topic. The candidate has one minute to prepare and they can make some notes if they wish, before speaking for between one and two minutes. The examiner then asks one or two questions on the same topic.
Part 3
The examiner and the candidate engage in a discussion of more abstract issues which are thematically linked to the topic in Part 2. The discussion lasts between four and five minutes.
The Speaking test assesses whether candidates can communicate effectively in English. The assessment takes into account Fluency and Coherence, Lexical Resource, Grammatical Range and Accuracy, and Pronunciation. More information on assessing the Speaking test, including Speaking Assessment Criteria (public version), is available on the IELTS website.
HOW IS IELTS SCORED?
IELTS results are reported on a nine-band scale. In addition to the score for overall language ability, IELTS provides a score in the form of a profile for each of the four skills (Listening, Reading, Writing and Speaking). These scores are also reported on a nine-band scale. All scores are recorded on the Test Report Form along with details of the candidate’s nationality, first language and date of birth. Each Overall Band Score corresponds to a descriptive statement which gives a summary of the English language ability of a candidate classified at that level. The nine bands and their descriptive statements are as follows:
9 Expert User - Has fully operational command of the language: appropriate, accurate and fluent with complete understanding.
8 Very Good User - Has fully operational command of the language with only occasional unsystematic inaccuracies and inappropriacies. Misunderstandings may occur in unfamiliar situations. Handles complex detailed argumentation well.
7 Good User - Has operational command of the language, though with occasional inaccuracies, inappropriacies and misunderstandings in some situations. Generally handles complex language well and understands detailed reasoning.
6 Competent User - Has generally effective command of the language despite some inaccuracies, inappropriacies and misunderstandings. Can use and understand fairly complex language, particularly in familiar situations.
5 Modest User - Has partial command of the language, coping with overall meaning in most situations, though is likely to make many mistakes. Should be able to handle basic communication in own field.
4 Limited User - Basic competence is limited to familiar situations. Has frequent problems in understanding and expression. Is not able to use complex language.
3 Extremely Limited User - Conveys and understands only general meaning in very familiar situations. Frequent breakdowns in communication occur.
2 Intermittent User - No real communication is possible except for the most basic information using isolated words or short formulae in familiar situations and to meet immediate needs. Has great difficulty understanding spoken and written English.
1 Non User - Essentially has no ability to use the language beyond possibly a few isolated words.
0 Did not attempt the test - No assessable information provided.
MARKING THE PRACTICE TESTS
Listening and Reading
The answer keys are on pages 151-160.
Each question in the Listening and Reading tests is worth one mark.
Questions which require letter / Roman numeral answers
? For questions where the answers are letters or Roman numerals, you should write only the number of answers required. For example, if the answer is a single letter or numeral you should write only one answer. If you have written more letters or numerals than are required, the answer must be marked wrong.
Questions which require answers in the form of words or numbers
? Answers may be written in upper or lower case.
? Words in brackets are optional - they are correct, but not necessary.
? Alterative answers are separated by a slash (/).
? If you are asked to write an answer using a certain number of words and/or (a) number(s), you will be penalised if you exceed this. For example, if a question specifies an answer using NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS and the correct answer is ‘black leather coat’, the answer ‘coat of black leather’ is incorrect.
? In questions where you are expected to complete a gap, you should transfer only the necessary missing word(s) onto the answer sheet. For example, to complete ‘in the ... ’, and the correct answer is ‘morning’, the answer ‘in the morning’ would be incorrect.
? All answers require correct spelling (including words in brackets).
? Both US and UK spelling are acceptable and are included in the answer key.
? All standard alternatives for numbers, dates and currencies are acceptable.
? All standard abbreviations are acceptable.
? You will find additional notes about individual answers in the answer key.
Writing
The sample answers are on page 161-172. It is not possible for you to give yourself a mark for the Writing tasks. We have provided sample answers (written by candidates), showing their score and the examiner’s comments. These sample answers will give you an insight into what is required for the Writing test.
HOW SHOULD YOU INTERPRET YOUR SCORES?
At the end of each Listening and Reading Answer key you will find a chart which will help you assess whether, on the basis of your Practice Test results, you are ready to take the IELTS test.
In interpreting your score, there are a number of points you should bear in mind. Your performance in the real IELTS test will be reported in two ways: there will be a Band Score from 1 to 9 for each of the components and an Overall Band Score from 1 to 9, which is the average of your scores in the four components. However, institutions considering your application are advised to look at both the Overall Band Score and the Bands for each component in order to determine whether you have the language skills needed for a particular course of study. For example, if your course has a lot of reading and writing, but no lectures, listening skills might be less important and a score of 5 in Listening might be acceptable if the Overall Band Score was 7. However, for a course which has lots of lectures and spoken instructions, a score of 5 in Listening might be unacceptable even though the Overall Band Score was 7.
Once you have marked your tests you should have some idea of whether your listening and reading skills are good enough for you to try the IELTS test. If you did well enough in one component but not in others, you will have to decide for yourself whether you are ready to take the test.
The Practice Tests have been checked to ensure that they are of approximately the same level of difficulty as the real IELTS test. However, we cannot guarantee that your score in the Practice Tests will be reflected in the real IELTS test. The Practice Tests can only give you an idea of your possible future performance and it is ultimately up to you to make decisions based on your score.
Different institutions accept different IELTS scores for different types of courses. We have based our recommendations on the average scores which the majority of institutions accept. The institution to which you are applying may, of course, require a higher or lower score than most other institutions.
- 新东方大愚文化图书官方店
- 扫描二维码,访问我们的微信店铺















